Objectives :
- Learn the fundamentals of content delivery network
Content Delivery Network

The Problem
Let's imagine you have an online platform for helping people learning the fundamentals on cloud skills, your application provide texts, images and videos. So far, the workflow is pretty simple :
After being authenticated, and based on their subscription, users have access to your platform
Users can browse the courses, read texts with images or play videos.
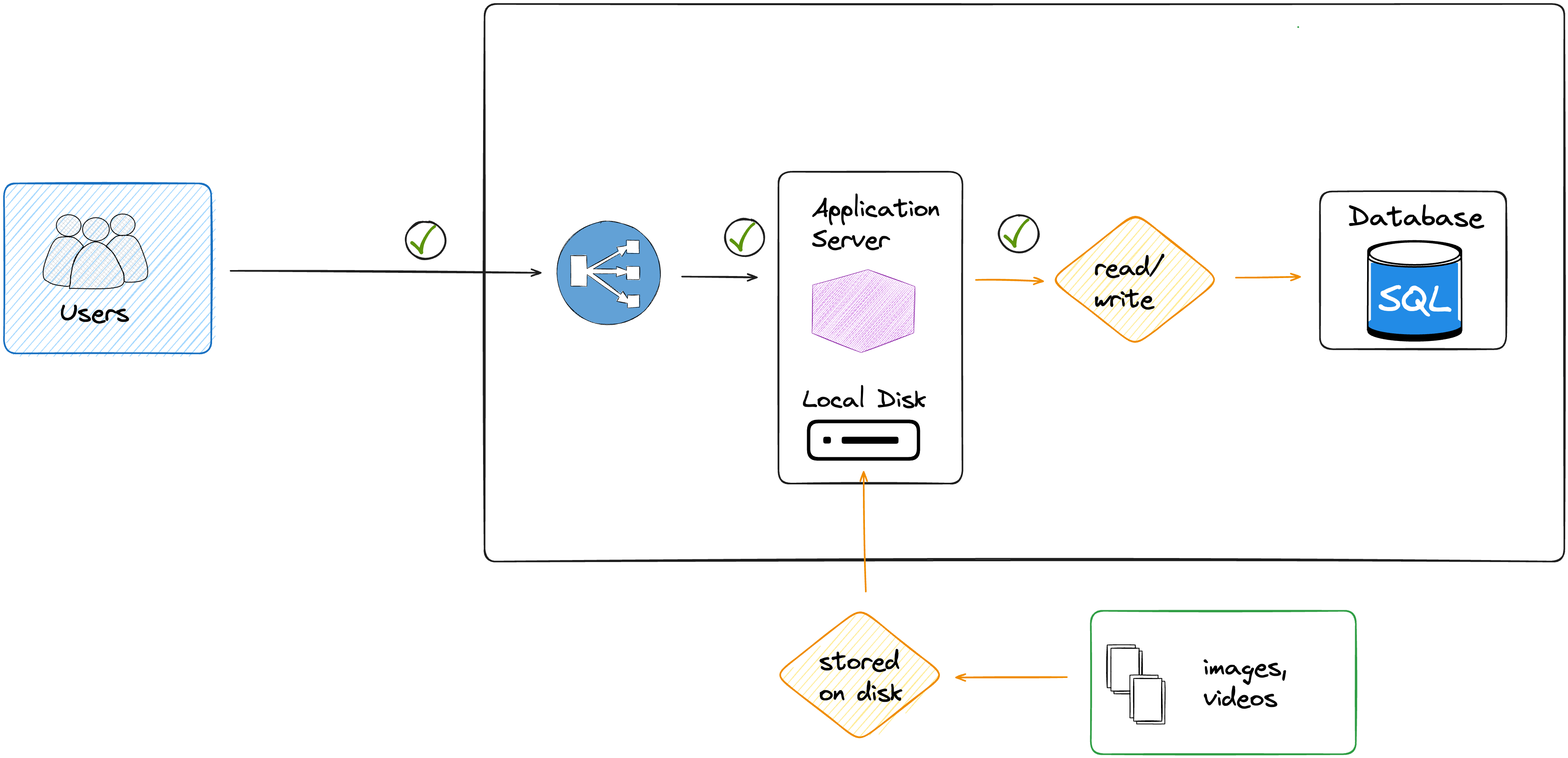
Right now, all the images and videos are stored on your local application server on a persistent disk
The informations about the users, the courses, etc, are stored securely on relational database.
As illustrated in the following diagram
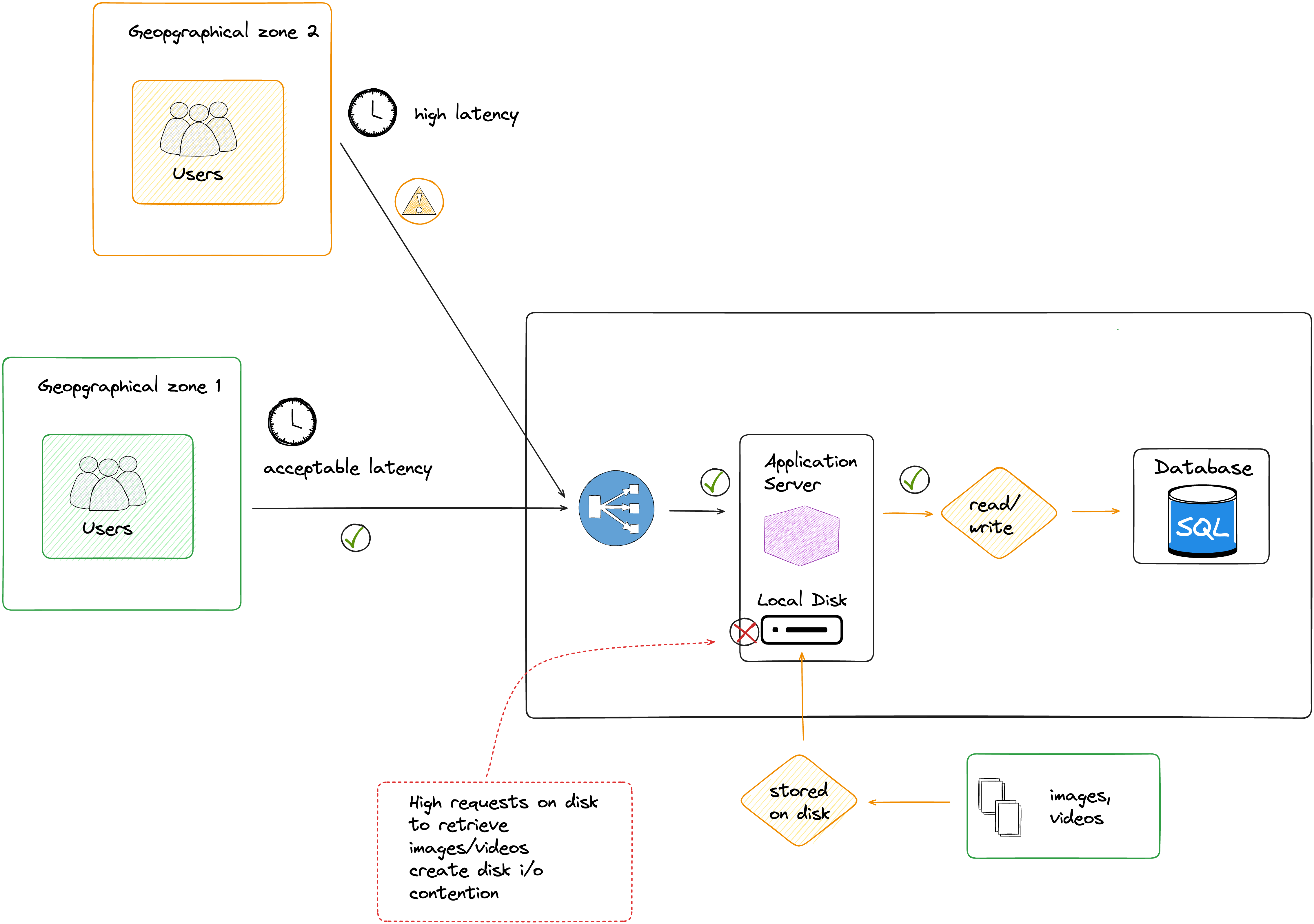
So far so good, until the traffic on your online platform get more and more important, additionally users have access from different remote geolocation.
There are more or more requests being handled by the application server, creating an access disk contention.
The application server takes longer to process requests
Users complain about their experiences, they can't play videos and the images takes longer to be loaded.
Users are frustrated with their experiences (slow response, etc..), and some decide to cancel their subscriptions.
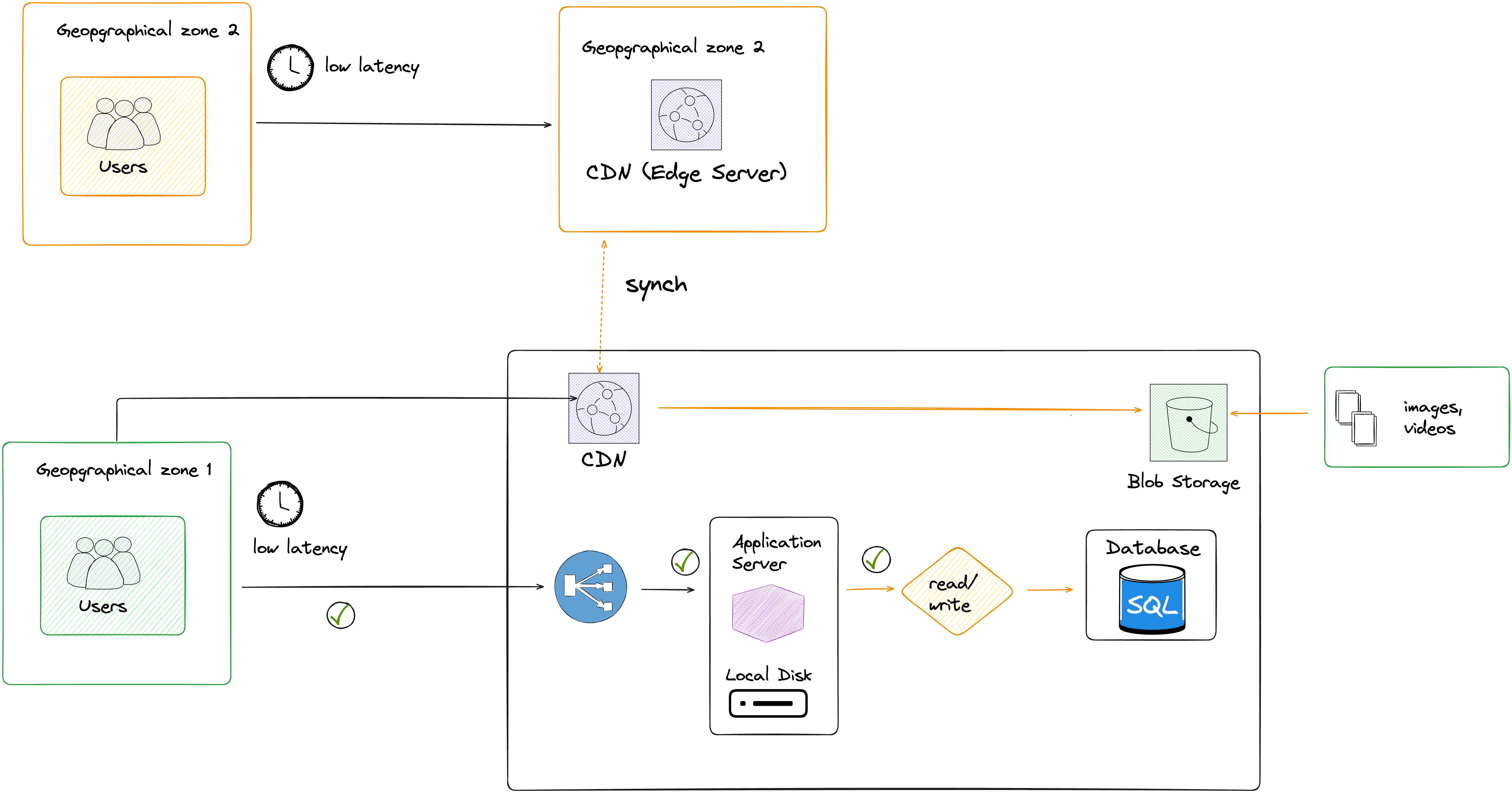
As illustrated in the following diagram, Users close to your infrastructure location experience good latency, but often get slow responses. Remote geo-location users always get slow response and complain the most.
There are few questions to ask ourselves

What's a Content Delivery Network (CDN) ?
A CDN is a large distributed system of servers, that will store your content (typically static content) on different locations.
The CDN will use the source content (where your static files are stored) as the origin.
When the users try to download the content (example : the link to a picture, or a video) the first time, the CDN reaches the origin server, then it stores (caches) copies of this content.
Next time the users try to download the content, the CDN retrieves it from its cache.
The main components of a CDN are :
Edge Servers : Servers located in different geographic locations, where the content is cached (copies of the static files).
Origin Servers : Server from which the edge servers download the original content. For instance, if you store your images or videos on a blob storage, the origin server is the blob storage.
Caching mechanism : You can define how long the content will be stored on the edge servers.
Security : Some CDNs include additional protection, like DDoS, WAF, rate limiting.
The main advantages of content delivery network :
The static content is delivered faster to users.
The process of retrieving static content (images, videos) is offloaded, freeing up resources on the origin server.
A better protection, if you experience a DDoS attacks, CDN provide the mechanisms to limit the impacts.
Based on what we've learned, and to improve our original architecture, we should implement a CDN, and copy the content/static files to a blob storage, as illustrated in this diagram :
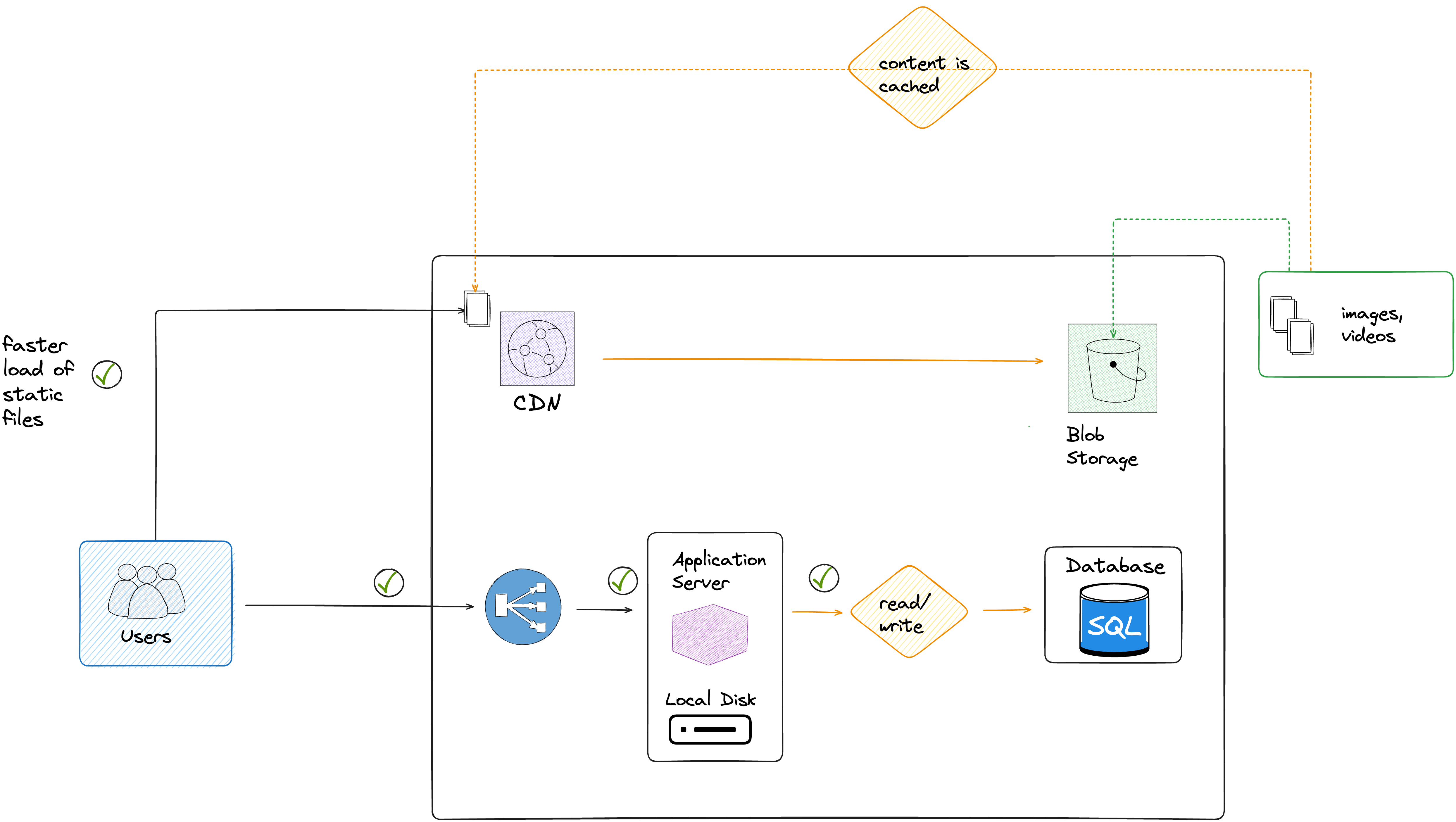
We've added new components in our architecture: the CDN and the blob storage
We move all the static files (images, videos, ..) to the blob storage, the main advantage is that it will first offload the application server, and it's way cheaper to store our files on a blob storage than on the persistent local disk.
Then we add a CDN, with the blob storage as the origin server.
Now that we have a CDN, the users from a different geo-location can have a faster access to the content, and a better experience.